CMSLTM/Scalability
From HP-SEE Wiki
Contents |
| Code author(s): George Kastellakis | |
| Application areas: Life Sciences | |
| Language: NEURON | Estimated lines of code: 2000 |
| URL: http://wiki.hp-see.eu/index.php/CMSLTM | |
Implemented scalability actions
Actions:
- Estimation of performance by running a smaller network in different number of processors
- Our simulations were implemented in the NEURON simulator, which uses MPI for parallelization. We weren't able to evaluate different MPI implementations, because it was only possible to compile NEURON with openMPI.
- Different compilers: We attempted to compile NEURON using intel compilers, however it was not possible due to incompatibilities. Although a precompiled binary is provided in the system, NEURON needs to recompile its own modules every time a change is made, therefore it is not possible to run the intel-compiled binary.
Benchmark dataset
The simulation consisted of a network configuration that was smaller than the one used in production.
Hardware platforms
Simulations were run on HPCG/BG in Sofia, Bulgaria.
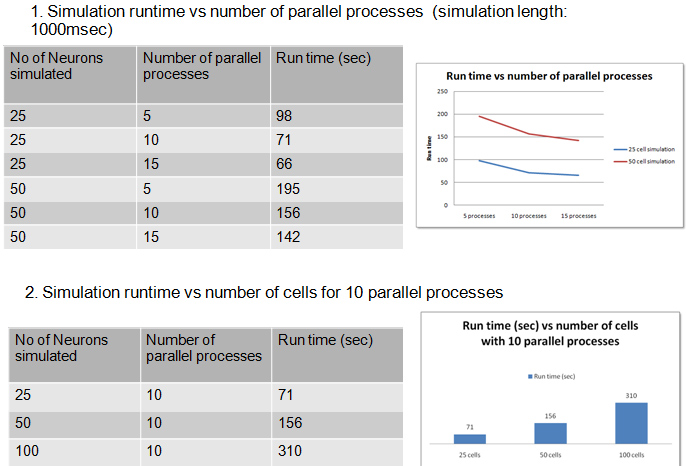
Execution times
Simulation times and graphs for different numbers of simulated neurons and number of computational nodes are shown below
Memory Usage
Memory usage is stable < 2GB as our application is not memory-intensive.
Profiling
We could not perform profiling due to lack of profiling support by the underlying platform (NEURON)
Communication
Interprocess communication through MPI. OpenMPI was the MPI implementation we used. We were unable to compile NEURON to work correctly with other MPI implementations.
I/O
We did not perform benchmarks, as our application is not IO-intensive
CPU and cache
No data
Derived metrics
Analysis
Our simulations show sub-linear scaling as new computational nodes are added. We identified optimal configurations that compromise between simulation size and number of nodes.