SIMPLE-TS 2D
From HP-SEE Wiki
General Information
- Application's name: Semi-Implicit Method for Pressure-Linked Equations - Time Step
- Application's acronym: SIMPLE-TS 2D
- Virtual Research Community: Computational Physics [A2]
- Scientific contact: Dr. Kiril Shterev, kshterev@imbm.bas.bg
- Technical contact: Dr. Kiril Shterev, kshterev@imbm.bas.bg
- Developers: Dr. Kiril Shterev and Prof. Stefan Stefanov, Department of Complex and Multiphase Flow, Institute of Mechanics - BAS, Bulgaria
- Web site: http://www.imbm.bas.bg/index.php/en_US/pressure-based-finite-volume-method
Short Description
Short description: Micro mechanical devices are rapidly emerging technology, where new potential applications are continuously being found. A simulation of internal and external gas flows in or aroundthese devices is important for their design. The flow motions described on the basis of the Navier-Stokes-Fourier compressible equations with diffusion coefficients determined by the first approximation of the Chapman-Enskog theory for the low Knudsen numbers.The gas flows are characterized with areas of low speed flows (low Reynolds numbers). The flows can go from high speed supersonic to very low speed regimes down to the incompressible limit. This made the pressure based numerical methods very suitable to be used for calculation of this kind of gas flows. The finite volume method SIMPLE-TS (a modification of SIMPLE created by K. S. Shterev and S. K. Stefanov) is used.
Problems Solved
Steady and unsteady flow past square in a microchannel.
Scientific and Social Impact
Micro mechanical devices are rapidly emerging technology, where new potential applications are continuously being found. A simulation of internal and external gas flows in or aroundthese devices is important for their design.
Collaborations
- Institute of Mechanics - BAS
- Institute of Information and Communication Technologies - BAS
Beneficiaries
Number of users
Development Plan
- Concept: The concept was done before the project started
- Start of alpha stage: It was done before the project started
- Start of beta stage: It was done before the project started
- Start of testing stage: M1 – M8
- Start of deployment stage: М9-М11
- Start of production stage: М12
Resource Requirements
- Number of cores required for a single run: Strongly depend from calculated problem (from 1 to 600)
- Minimum RAM/core required: Strongly depend from calculated problem (from 10MB to 2GB per core)
- Storage space during a single run: Strongly depend from calculated problem (from 10MB to 200GB)
- Long-term data storage: 50GB
- Total core hours required: .
Technical Features and HP-SEE Implementation
- Primary programming language: C++
- Parallel programming paradigm: SIMD
- Main parallel code: MPI
- Pre/post processing code: None
- Application tools and libraries: C++ compiler
Usage Example
Source code, some examples and publications describing the algorithm and parallel organisations are freely available on: http://www.imbm.bas.bg/index.php/en_US/pressure-based-finite-volume-method
Infrastructure Usage
- Home system: .
- Applied for access on: .
- Access granted on: .
- Achieved scalability: .
- Accessed production systems:
- .
- Applied for access on: .
- Access granted on: .
- Achieved scalability: .
- Porting activities: Access has been provided to the development team not only to high performance cluster with Infiniband interconnect but also to the IBM Blue Gene machine and to a small cluster with GPGPU capability. The issues that arose when porting the application to these architectures were discussed and paths to mitigate the problems were proposed. In the case of IBM Blue Gene the main issue is the high number of processes that need to communicate with one another, which lead to the idea to move to a hybrid OpenMPI-MPI programming model in order to achieve scalability beyoung 1024 CPU cores.
- Scalability studies: .
Running on Several HP-SEE Centres
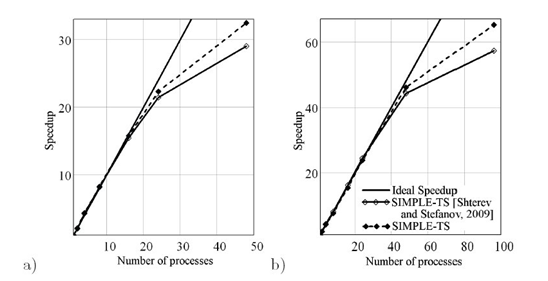
- Benchmarking activities and results: Two versions of the SIMPE-TS-2D application were created –(i) before optimization and (ii) after optimization. The speedup after the MPI realizations of the both versions was measured on HPCG cluster at IICT-BAS. The results for speedup up to 100 cores and for two kind of meshes: (i) 500X100 cells and (ii) 1000X200 cells are shown below.
The next step is to investigate speedup of both versions of the application using the supercomputer Blue Gene/P.
- Other issues: no
Achieved Results
Publications
- Kiril S. Shterev, Stefan K. Stefanov, and Emanouil I. Atanassov, A parallel algorithm with improved performance of Finite Volume Method (SIMPLE-TS), ”, 8th LSSC’11, June 6-10, 2011, Sozopol, Bulgaria, accepted to LNCS, 8 pages, 2011.